Client
A SaaS company running high-traffic applications across AWS/GCP, facing rising cloud bills and inefficient resource usage.
Monthly cloud spending had grown beyond expectation due to:
-
Over-provisioned instances
-
Idle resources
-
Unoptimized storage tiers
-
Poor autoscaling configuration
-
No visibility into service-level costs
The goal was to reduce cloud costs without reducing performance.
Project Overview
We executed a detailed FinOps-driven cloud cost optimization initiative involving:
-
Rightsizing virtual machines / compute instances
-
Optimizing storage tiers and lifecycle policies
-
Configuring efficient autoscaling
-
Using AWS Cost Explorer / GCP FinOps dashboards
-
Eliminating unused and idle resources
-
Improving observability and cost tracking
The focus:
Cut cost, maintain performance, improve efficiency.
Key Challenges
1. Over-Provisioned Compute Instances
Many services used:
-
Large EC2 / GCE instance types
-
Under 20–30% CPU usage
-
No autoscaling
2. Unoptimized Storage
-
Large S3 / GCS buckets with mixed cold/hot data
-
EBS disks unused or attached to terminated VMs
-
Logs consuming expensive storage
3. Missing Autoscaling & Scheduling
Workloads were running 24/7 even when traffic dropped drastically at night/weekends.
4. Lack of Visibility
Team had no clear breakdown of:
-
Application-level cost
-
Team-wise cost
-
Historical cost trends
-
Idle resource wastage
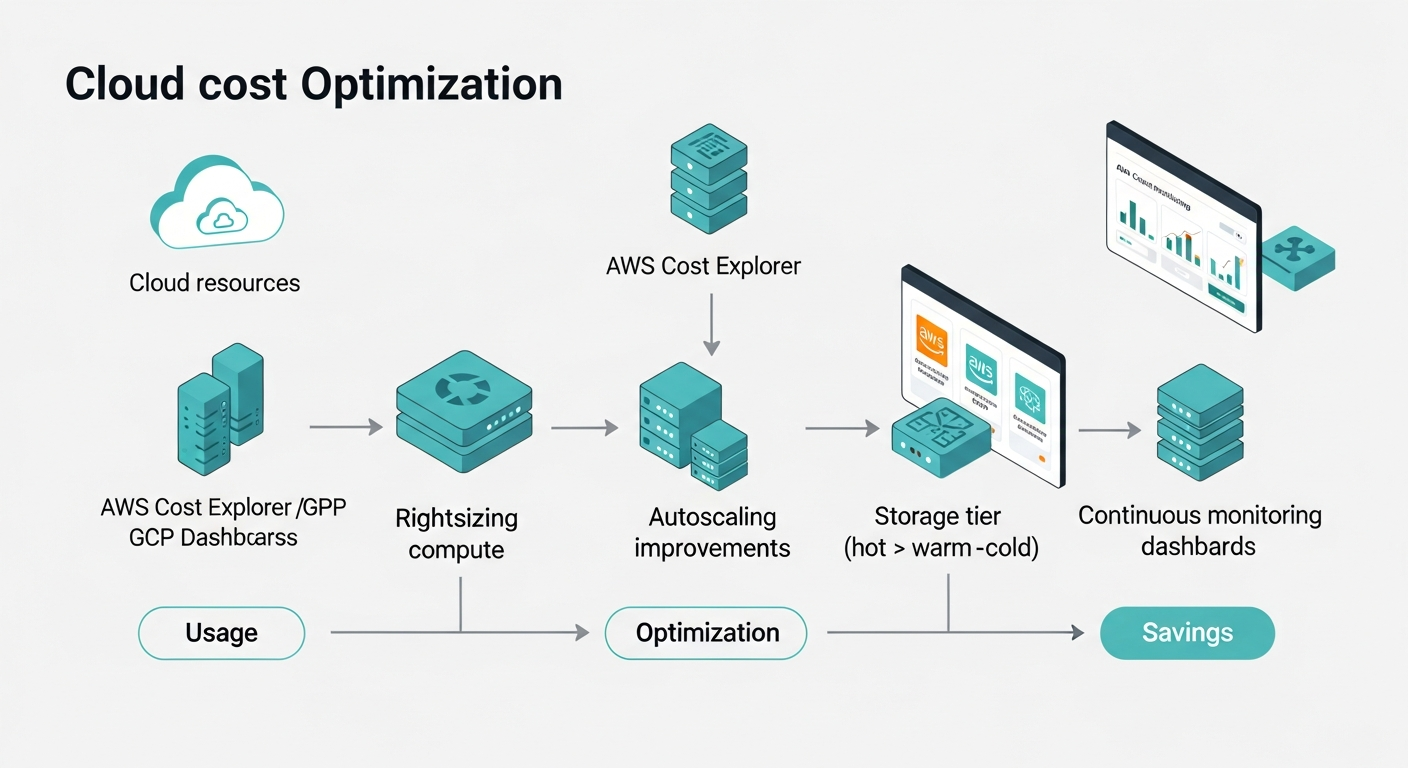
Our Solution
1. Rightsizing Compute Instances (AWS EC2 / GCP GCE)
We analyzed usage via:
-
AWS Cost Explorer
-
AWS Compute Optimizer
-
GCP Recommender
-
CloudWatch & Stackdriver metrics
Based on CPU, RAM, and I/O usage, we:
-
Reduced instance sizes
-
Switched from general-purpose to compute/memory optimized
-
Migrated to ARM-based Graviton2/3 (AWS) or Tau T2D (GCP) where applicable
-
Consolidated workloads on fewer but appropriately sized machines
Result:
30–40% savings on compute without any performance drop.
2. Autoscaling Enhancements
We implemented/optimized:
-
Horizontal Pod Autoscaling (Kubernetes)
-
EC2 Auto Scaling Groups
-
Instance cooldown periods
-
Predictive scaling rules
-
Scheduled scaling (reducing nodes at night)
This ensured:
-
Scale up during peak
-
Scale down during low-traffic hours
Result:
Over 25% savings on variable workloads.
3. Storage Optimization
We optimized all major storage services:
AWS
-
Moved large S3 data to Glacier & Infrequent Access
-
Enabled lifecycle rules
-
Deleted unused EBS volumes
-
Converted gp2 → gp3 for cost reduction
GCP
-
Migrated data to Nearline/Coldline
-
Cleaned old logs
-
Reduced SSD dependency where not needed
Result:
20–35% reduction in storage spending.
4. Eliminating Unused Resources
We removed or decommissioned:
-
Old snapshots
-
Orphaned IPs
-
Idle VMs
-
Unused load balancers
-
Legacy autoscaling configs
-
Dead Kubernetes namespaces
This provided immediate, no-risk cost savings.
5. Using FinOps Tools (AWS Cost Explorer / GCP Cost Management)
We built dashboards to track:
-
Per-service cost
-
Environment-wise cost
-
Month-over-month trends
-
Wastage metrics
-
Team-level spending
Configured:
-
Alerts for unusual usage spikes
-
Forecasting for budgeting
-
Reports for management
Provided full visibility into where cloud money goes.
6. Introducing Cost Governance & Best Practices
We established:
-
Tagging standards
-
CI/CD cost checks
-
Developer training
-
Rightsizing policy
-
Scheduled reviews
Created a culture of cost awareness, not just technical fixes.
Architecture Diagram (Text Version)
Results & Impact
💰 Total Cloud Cost Saving: 35–55%
Achieved without compromising reliability or performance.
⚡ Optimized Performance
Better autoscaling → more stable workloads under load.
🧠 Improved Visibility
Teams now understand where cost originates.
🧹 Zero Wastage
Unused instances, volumes, and IPs were fully cleaned up.
🧱 Future-Proof Cost Governance
Clear policies ensure costs stay low over time.
Conclusion
Through a structured cloud cost optimization strategy including rightsizing, autoscaling, storage tuning, and FinOps tooling — we enabled the client to cut costs dramatically without sacrificing performance.
The platform is now:
-
More efficient
-
More predictable
-
Easier to scale
-
Much cheaper to operate
A long-term FinOps foundation is now in place for continued savings.

Written by
Oliver Thomas
Oliver Thomas is a passionate developer and tech writer. He crafts innovative solutions and shares insightful tech content with clarity and enthusiasm.